Minimize the Risk of Being One Weak or Stolen Password Away From a Data Breach
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication today to secure your business.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Multi-factor authentication is a process where a user is prompted, during the sign-in process, for an additional form of identification, such as to enter a code on their cellphone or to provide a fingerprint scan.
If you only use a password (even a complex one) to access your email or applications, it leaves you vulnerable to a cyber attack. If the password is weak or has been exposed elsewhere, the application you are trying to sign into really has know way of knowing if it is truly you, or is it an attacker? When you require a second form of authentication, security is increased as this additional factor isn't something that's easy for an attacker to obtain or duplicate.
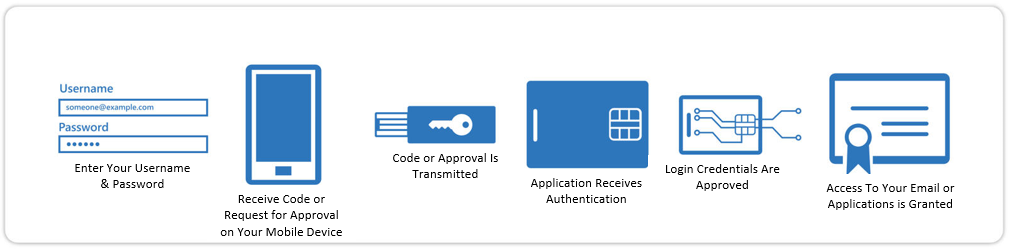
How Does MFA Work?
Why Use MFA?
It’s More Secure Than Passwords
According to the Verizon 2021 Data Breach Incident Report, over 61% of all breaches are caused by stolen or compromised credentials.
Hackers are adept at leveraging any employee’s breached credentials to access sensitive systems, leverage corporate email for social engineering, spear phishing attacks or other financial fraud, or export corporate data from systems.
Ensure Compliance
HIPAA, PCI, SOX- just a few of the compliance standards that require MFA be enabled to meet security compliance.
Depending on the industry, failing to implement MFA can lead to significant penalties. In financial services, for example, MFA non-compliance may result in regulatory punishment, monetary penalties and even class action lawsuits.
Remote Workforces
In the rush to shift to remote work during COVID-19, 85% of organizations say they sacrificed security to quickly get employees setup to work from home; often times using personal devices.
Personal devices often don’t have the powerful protection installed on them that company-owned machines do. That means that these attacks go undetected until it’s too late.
Ready to get MFA?